Diabetes: Definition, Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Do you know? The number of diabetic patients in the world is increasing day by day. The World Health Organization estimates, about 422 million people worldwide have diabetes now. Surprisingly, 40 percent of them are in India. As of 2020, the numbers place the country among the top 10 countries for people with diabetes, coming in at number two with an estimated 77 million diabetics.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a clinical condition where a person’s blood glucose level (commonly called as sugar) is above the normal limits.
What is Glucose?
Glucose is the major energy supplier which is essential for the normal functioning of all the major organ system in the body.
Where do we get the glucose?
Majority of the supply of glucose to the human body is from external sources (diet) and minor production from liver and kidney.
What is the major regulator of glucose in the human body?
The major regulator of glucose in the human body is a hormone named as Insulin.
Where is insulin produced from?
Insulin is produced from the organ called pancreas (specifically beta cells in the pancreas).
How insulin regulates the blood glucose?
Insulin moves the glucose from the blood into the cells (specifically liver, muscle, and fat tissues).
How does diabetes occur?
Diabetes mellitus occurs due to 2 main reason,
- Reduced insulin production or secretion from the pancreas.
- Poor insulin action (insulin resistance) of the level of liner muscles or fat tissues.
What are the types of diabetes?
- Type 1 diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes
- Pancreatic diabetes
- Pregnancy induced diabetes
- Maturity onset diabetes young mody
- Syndromic diabetes
Common diabetes seen in our community?
More than 90% of the diabetes seen in our community is Type 2 diabetes.
Risk factors for Type 2 diabetes :
You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you have:
- Obese or Overweight
- Age 45 or older
- Family history of diabetes
- African American, Alaska Native, American Indian, Asian American, Hispanic/Latino, Native Hawaiian, or pacific islander.
- High blood pressure
- Low level of HDL (good) cholesterol or a high level of triglycerides
- History of gestational diabetes or gave birth to a baby weighing 9 pounds or more
- Not physically active
- History of heart disease or stroke
- Depression
- Polycystic ovary syndrome, also called PCOS
- Acanthosis nigricans-dark, thick, and velvety skin around your neck or armpits
Symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus?
- Increased thirst
- Increased frequency of urination
- Increased hunger
- Weight loss
- Recurrent infections
- Excessive tiredness
- Blurred vision
- Delay in healing
How to diagnose?
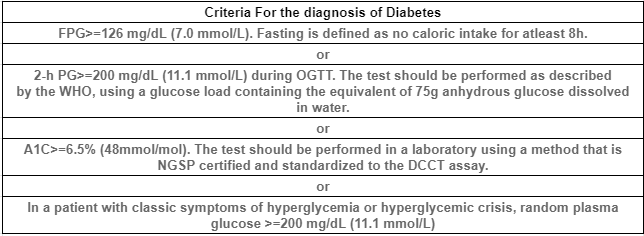
Treatment :
- Lifestyle Modification :
- Physical Activity
- Diet Modification
- Medications :
- Tablets
- Insulin
Is Type 2 diabetes preventable?
Yes, according to the data from international diabetes federation, more than 80% of the Type 2 diabetes is preventable with adoption of healthy lifestyle habits.
Is Type 2 diabetes reversible?
Yes, with appropriate lifestyle modifications (diet and physical activity) and expert guidance from a specialist doctor (Endocrinologist), Type 2 diabetes can be reversed at the early stage of diagnosing the condition.
What are the complications of diabetes?
1.Small Vessel Damage
- Retina (eye)
- Kidney
- Nerve
2. Large Vessel Damage
- Heart Attack
- Stroke
- Foot Disease
How to reduce the risk of developing complications of diabetes?
Strict blood glucose control with an HbA1c less than 7% will help to reduce the risk of complications.
What is HbA1c?
HbA1c or Glycated Hemoglobin is a marker for the previous 3 months average of blood glucose.
How often HbA1c should be tested?
At least once in every 3 months or even earlier as directed by the specialist doctor.
How to screen for the development of complications in diabetes?
The following screening test should be done at least annually
- Retinal Examination
- Foot Sensation
- Kidney Function Test
- ECG & Echocardiography / Treadmill Test (TMT) for cardiac evaluation
- Liver Function Test
How to care for prevention of foot problems in diabetes?
- Daily examination of the feet for injuries, fissures, swelling, foot shape changes etc…
- Examine the space between toes for any fungal infections.
- Use proper diabetic foot wear (made out of microcellular rubber or poly urethane (MCR/MCP).
- Patients with diabetic neuropathy should not dip your feet in warm water.
- Appropriate moisturizers as advised by your specialist doctor should only be applied on the feet.
If you notice diabetes or other symptoms related to the disease, seek medical help immediately
